Unit 3 Overview: Cultural Patterns & Processes
7 min read•june 18, 2024
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Unit 3 Overview: Cultural Patterns & Processes 👨👩👲👳💂
3.0: All About Culture!
Think about what defines your community and the people in it. What do the people in your community have in common with each other? What activities and values do you all have in common? Customs, beliefs, laws, social standards, and religious traditions are all examples of cultural values. In this unit, we will tackle a very complex yet simple question—what is culture?
Unit Preview (Try to answer these questions!)
- How does the culture of an area affect the natural environment? 🌲
- How does the culture of an area affect public perception of a region? 👀
- Why are some areas more culturally diverse than others? 🗺️
- What is globalization, and how does it affect local cultures in a given area? 🌍
- How can culture affect the rights of women? 👩
- How do cultures blend and interact with each other? 💬
Cultural Landscapes
Take a look at your neighborhood 🏡 or city skyline 🌆. What makes your community look different from others? The unique cultural landscape of an area is the impact of cultural ideas and beliefs on the physical environment. Observing cultural landscapes can help geographers better understand the culture of a place.
For example, a community located in a rural 👨🌾 area may look different from one located in an urban 👩🏻💼 area in terms of the types of buildings and infrastructure present, the layout of the community, and the availability of resources and amenities. A community with a diverse population may look different from one with a more homogenous population in terms of the languages spoken, cultural practices, and traditions observed. A community with a rich history ⛪ may have historical landmarks or sites that distinguish it from other communities, and a community with a strong economic base 💰 may have different types of businesses and industries present. Ultimately, the specific characteristics that make a community look different from others will depend on the unique combination of factors that shape its identity and sense of place.
🎥 Watch: APHUG - Cultural Landscapes
Sense of Place
Sense of Place refers to the relationship between people, their communities, and the physical environment. In other words, sense of place is the feeling of attachment towards a place.
🔗 Take a moment to answer this question: How does a strong sense of place affect where people choose to live?
A strong sense of place can be an important factor in where people choose to live, as it can contribute to a sense of belonging and community 🤝. People may be attracted to a place that has a unique history or cultural identity, or that offers a particular type of natural environment 🌳 or amenities. A strong sense of place can also contribute to a sense of stability and security 🔒, as people may feel more connected to and invested in their community. On the other hand, a lack of a strong sense of place may discourage people from living in a particular location. If a community lacks a clear identity or sense of purpose, or if it lacks resources or amenities that are important to its residents, it may be less attractive 😔 to potential residents. Overall, a strong sense of place can be a powerful factor in shaping the attractiveness of a community as a place to live.
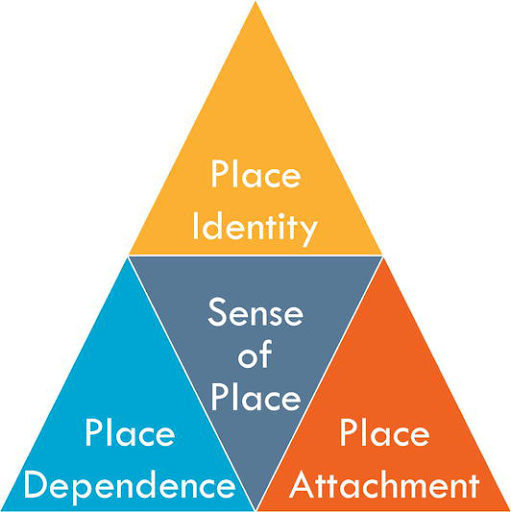
Image Courtesy of InTech Open
Placelessness 🌐😕
What happens when a city or community does not have a unique cultural landscape? The term for when a community lacks a unique identity is called placelessness. In other words, a placeless city is indistinguishable from other similar places in its cultural landscape or appearance.
Placelessness can be caused by a variety of factors, including rapid social and cultural change 🌀, economic development, and the loss of traditional ways of life. It can also be the result of the physical transformation of a place, such as through the development of new infrastructure or the demolition of historical landmarks.
For example, think about a gas station ⛽ next to a major highway. Standardized gas stations across the United States are made to look the same. Thus, people lack a sense of attachment to these regions.
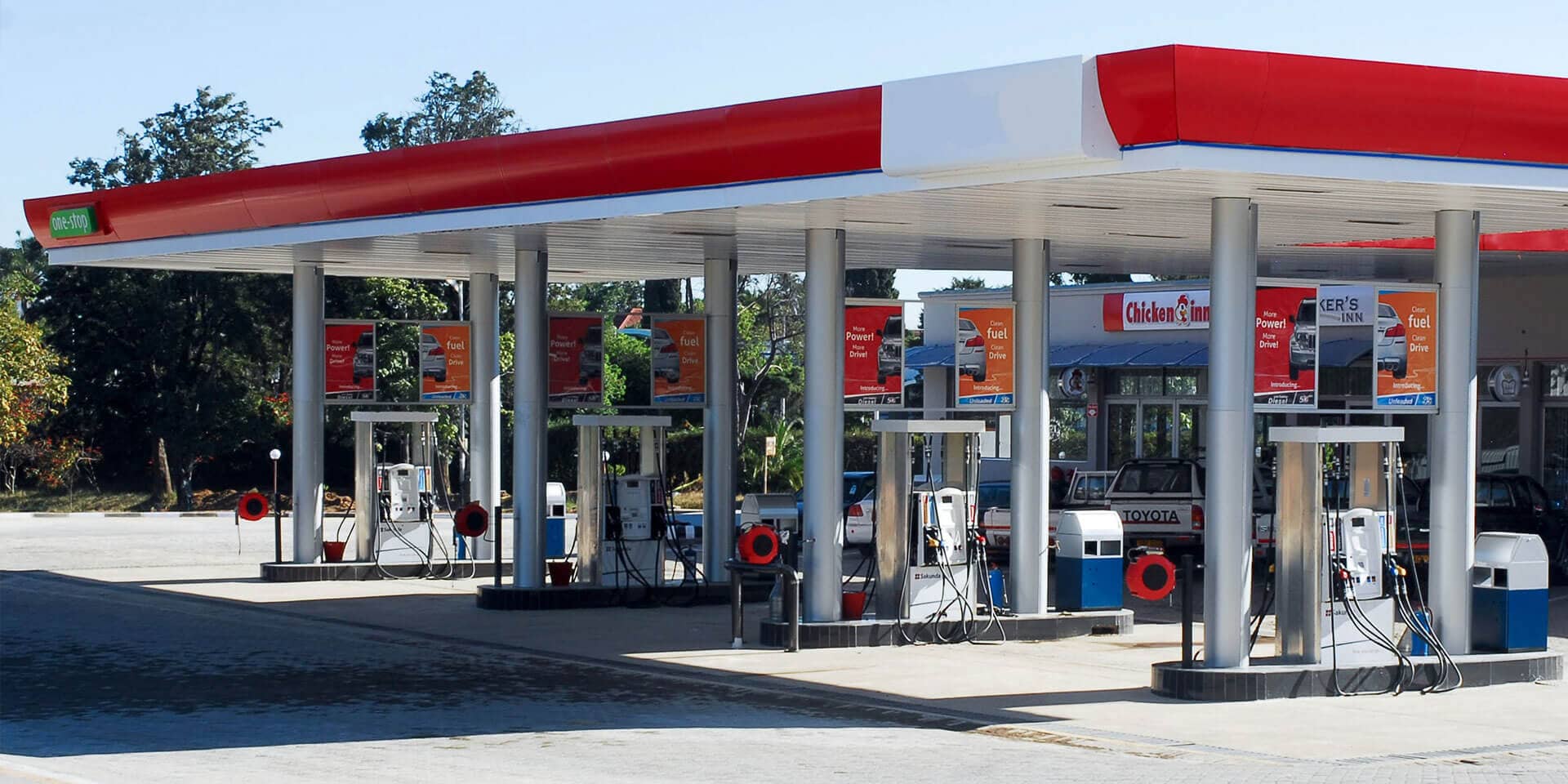

Image Courtesy of LS Retail
Globalization 🌏 refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world's economies, cultures, and populations. It is a process that has been driven by advances in communication 💬, transportation 🚌, and technology 💻, which have made it easier for people, goods, and ideas to cross national and cultural boundaries.
Globalization has had a significant impact on culture, as it has facilitated the exchange of ideas, goods, and services 💰💭🛎️ across national and cultural boundaries. 👨💭👳 In some cases, this blending of cultures and ideas can be a positive force that creates new, syncretic cultures.
On the other hand, globalization can hinder existing local cultures by promoting a globally mainstream culture. As more and more people adopt global culture for economic or social reasons, people practicing local cultures and languages will need to make a tough decision: either blend their culture with the mainstream or be forced out of existence.
🎥 Watch: APHUG - Globalization I & Globalization II

Image Courtesy of JAN NEDERVEEN PIETERSE
Culture & Gender 👫
Culture and gender are closely intertwined 🪢, as cultural norms and expectations often shape the roles and behaviors of men and women within a society. These norms and expectations can vary significantly from one culture to another, and they can also change over time within a single culture.
In many cultures, there are clear gender roles and expectations for men and women. These roles and expectations may be based on biological differences between men and women, or they may be based on cultural and social constructions of what it means to be male 👨 or female 👩.
Cultural norms and expectations regarding gender can influence a wide range of aspects of people's lives, including their dress, their behavior, their employment and education opportunities, and their relationships. In some cultures, there may be a strong emphasis on traditional gender roles (patriarchy 👔), while in others, there may be more flexibility 👩⚕️ and fluidity in terms of how men and women are expected to behave.
Understanding the ways in which culture and gender intersect is important for a number of reasons, including for the promotion of gender equality and for the understanding of how cultural influences shape gender roles and expectations.
Types of Diffusion 💥📲📺💻✈💥
There are several ways in which culture can diffuse (spread) from its hearth (origin) to other places. To understand why English is widely spoken 💬 throughout the world, why Christianity ⛪ and Islam 🕌 have millions of followers, and why pop culture trends go viral 📱📈 on a regular basis, we use relocation 🏃and expansion diffusion (hierarchical, contagious, and stimulus).
🎥 Watch: APHUG - Diffusion of Religion & Language
Cultural Interactions 🌎👨👩👲👳🌎
Acculturation, assimilation, and multiculturalism all relate to how cultures spread and influence each other.
Acculturation refers to the process of cultural change that occurs when groups of people with different cultures come into contact with one another. It is a common phenomenon that has occurred throughout human history, and it can involve the exchange of ideas, behaviors, and cultural practices between different groups. This results in a blending of cultures that mix elements of both. 🤝
Assimilation refers to the process by which a minority group or culture adopts the practices and values of the dominant group or culture. It is a type of acculturation that occurs when a minority group becomes integrated into the dominant culture, and it often involves the abandonment of the minority group's own cultural practices and values. In response to this, a growing multiculturalism movement in multiethnic nations seeks to represent all cultures equally and ensure that all people can live in harmony.
Languages 🗣 & Religions 🛐
There are over 7,000 languages in the world today, but many are at risk of dying due to the increasing influence of English and other influential lingua francas. Globalization—coupled with enhanced communication 📱💻📶 and transportation ✈🚁🚀🚊🚅 technologies—places increased pressure on lesser-used languages and cultural practices due to increased interactions between previously isolated people groups.
The five major global religions are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Judaism. Hinduism and Judaism haven’t spread far from their origin, but the other three—especially Christianity and Islam—are diffused throughout the world as a result of colonization, trade, and international migration. Like language, many world religions face a constant threat of losing followers due to the rise of cultural globalization.
🎥 Watch: APHUG - Religion and Culture
So, What is "Culture"?
In summary, culture influences the way that people within a group or society think, feel, and behave, and it shapes the way that the group or society responds to various situations. Culture can be seen as the "glue" that holds a group or society together, as it provides a common set of references and a shared way of life for its members. Culture is also a way of transmitting knowledge and values from one generation to the next, and it is often an important factor in shaping an individual's identity. There are many different aspects of culture, including language, religion, customs, food, music, and art, and these aspects can vary significantly from one culture to another. Culture is constantly evolving and changing, as people adapt to new situations and experiences.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.