Danna Esther Gelfand
Danna Esther Gelfand
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Sense of Place
Sense of place is the perception based on our emotional connection and association with a certain place).
Placelessness is the similarity of places of popular culture everywhere and the loss of a place’s unique identity due to the influence of popular culture and globalization.
Popular culture promotes uniformity in the landscape, lack of traditional value, or cultural uniqueness due to the widespread popularity of specific ideas, places, etc. For instance, chain-fast food restaurants are located within close proximity to each other. Skyscrapers diffuse signifying modern, urban, city landscapes.
Having a sense of place greatly impacts an individual's sense of identity, well-being, and connection to their community. An individual with a strong sense of place generally has a greater sense of belonging and attachment to their community. This can lead to increased feelings of security and happiness. Values, beliefs, and behaviors are also affected by a sense of place.
Having a minuscule sense of place, or placelessness can lead to feelings of isolation, disconnection, and rootlessness.
Sense of place can change depending on the person, and it can also change depending on where a person is at in their lives, things they experience, connections they form, and places they visit.
Environmental Determinism
Environmental determinism was theorized by Ellsworth Huntington who stated that the physical environment controls/determines behavior among humans. This theory has a few implications such as that it does not consider that the main location of cultural hearths is in lower latitude regions and citizens in tropical civilizations have established advanced societies which counter this interpretation.

image courtesy of tandfonline
This idea can lead to harmful stereotypes and discrimination because it implies that certain groups of people are inherently inferior due to where they are located or their climate. The theory can also be used to justify exploitative practices such as colonization and resource extraction. Environmental determinism can also lead to the neglect of social, economic, and political factors that largely shape society and development.
Possibilism states that the physical environment establishes limitations on the possibilities of populations. This theory is more accepted than environmental determinism yet does not explain how we have flourished beyond our environment to progress, innovate, and evolve technologically.
Cultural Determinism
Cultural determinism states that the environment does not play a role in determining human behaviors or placing restrictions but rather humans place their own cultural restrictions. A culture region is a portion of the earth's surface with inhabitant populations sharing distinctive cultural characteristics.
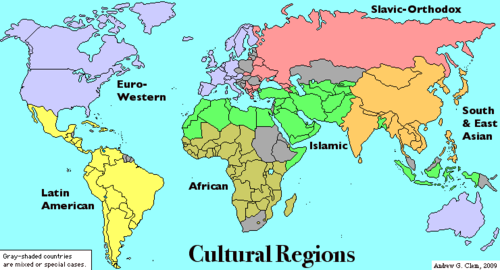
image courtesy of google images
Differences among cultural groups are greater than differences among individuals of a certain cultural group. Environment forms culture.
Western cultures and more developed countries (MDCs) are dominant in their popular cultural trends including the US, U.K, and Japan in regards to television broadcasting, social media, music, industry, fashion, etc. LDCs (less developed countries).
Indigenous languages such as Basque, Welsh, Quechua, etc struggle to be maintained however increased nationalism, tourism, and governmental policies allow minority languages to be kept despite the rise of globalization (in some circumstances). There are also extinct languages due to globalization including Latin. Additionally, endangered languages like Yiddish.
In order to support the growth of popular cultures, resources must be acquired to supply the demand which leads to pollution, environmental degradation, use of nonrenewable resources such as fossil fuels which place harm on the future as well in terms of global warming, greed amongst big businesses and corporations, destruction of traditional historic landscapes, etc.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Cultural Landscapes
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
✍️Free Response Questions (FRQ)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.