Jillian Holbrook
Sadiyya Holsey
Dalia Savy
Jillian Holbrook
Sadiyya Holsey
Dalia Savy
AP Psychology 🧠
334 resourcesSee Units
Overview of Research Methods
There are various types of research methods in psychology with different purposes, strengths, and weaknesses.
| Research Method | Purpose/Definition | Strength(s) | Weaknesses |
| Experiments🧪 | Manipulates one or more independent variables to determine the effects of certain behavior. | (1) can determine cause and effect (2) can be retested and proven | (1) could have potential ethical issues (2) artificial environment creates low realism (people know they are being researched, which could impact what they say and do) |
| Correlational Studies 📈 | Involves looking at the relationships between two or more variables and is used when performing an experiment is not possible. | (1) easier to conduct than an experiment (2) can be used when an experiment is impossible. For example, a researcher may want to examine the relationship between school grades and Adderall. It would not be ethical to force students to take high doses of Adderall. So, one can only rely on participants’ responses | cannot determine cause and effect |
| Survey Research 💭 | The collection of information reported by people about a particular topic. | (1) cost-effective (2) mostly reliable | (1) low response rates (2) can’t verify the accuracy of an individual’s response |
| Naturalistic Observations👀 | A researcher observes a subject's behavior without intervention. | natural setting is more reliable than a lab setting | (1) people behave differently when they know they are being watched, which could impact the results (Hawthorne effect) (2) two researchers could see the same behavior but draw different conclusions |
| Case Studies 💼 | A case study is an in-depth study of an individual or a small group. Usually, case studies are done on people with rare circumstances. For example, a girl named Genie was locked in her room, causing a delay in development. Researchers did a case study about her to understand more about language and human development stages. | provides detailed information | (1) cannot generalize results to a wider population (2) difficult to replicate (3) time-consuming |
| Longitudinal Studies ↔️ | The same individuals are studied over a long period of time from years up to decades. | (1) can show the effects of changes over time (2) more powerful than cross-sectional studies | (1) require large amounts of time (2) expensive |
| Cross-Sectional Studies | A cross-sectional study examines people of different groups at the same time. For example, studying people that are different ages at the same time to see what differences can be attributed to age. | (1) quick and easy to conduct (2) generalizable results | (1) difficult to find a population that differs by only one factor (2) cannot measure changes over time |
Examples
Experiment 🧪
Whenever researchers want to prove or find causation, they would run an experiment.
An experiment you'll learn about in Unit 9 that was run by Solomon Asch investigated the extent to which one would conform to a group's ideas.
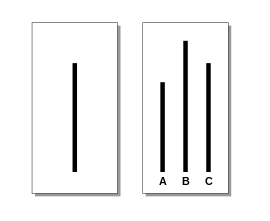
Image Courtesy of Wikipedia.
Each person in the room would have to look at these lines above and state which one they thought was of similar length to the original line. The answer was, of course, obvious, but Asch wanted to see if the "real participant" would conform to the views of the rest of the group.
Asch gathered together what we could call "fake participants" and told them not to say line C. The "real participant" would then hear wrong answers, but they did not want to be the odd one out, so they conformed with the rest of the group and represented the majority view.
In this experiment, the "real participant" was the control group, and about 75% of them, over 12 trials, conformed at least once.
Correlational Study 📈
There could be a correlational study between anything. Say you wanted to see if there was an association between the number of hours a teenager sleeps and their grades in high school. If there was a correlation, we cannot say that sleeping a greater number of hours causes higher grades. However, we can determine that they are related to each other. 💤
Remember in psychology that a correlation does not prove causation!
Survey Research 💭
Surveys are used all the time, especially in advertising and marketing. They are often distributed to a large number of people, and the results are returned back to researchers.
Naturalistic Observation 👀
If a student wanted to observe how many people fully stop at a stop sign, they could watch the cars from a distance and record their data. This is a naturalistic observation since the student is in no way influencing the results.
Case Study 💼
A notable psychological case study is the study of Phineas Gage:
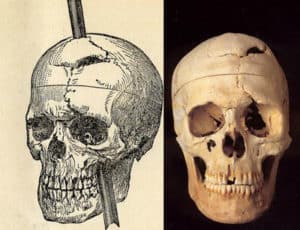
Image Courtesy of Vermont Journal
Phineas Gage was a railroad construction foreman who survived a severe brain injury in 1848. The accident occurred when an iron rod was accidentally driven through Gage's skull, damaging his frontal lobes. Despite the severity of the injury, Gage was able to walk and talk immediately after the accident and appeared to be relatively uninjured.
However, Gage's personality underwent a dramatic change following the injury. He became impulsive, irresponsible, and prone to outbursts of anger, which were completely out of character for him before the accident. Gage's case is famous in the history of psychology because it was one of the first to suggest that damage to the frontal lobes of the brain can have significant effects on personality and behavior.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🔎Unit 1 – Scientific Foundations of Psychology
🧠Unit 2 – Biological Basis of Behavior
👀Unit 3 – Sensation & Perception
📚Unit 4 – Learning
🤔Unit 5 – Cognitive Psychology
👶🏽Unit 6 – Developmental Psychology
🤪Unit 7 – Motivation, Emotion, & Personality
🛋Unit 8 – Clinical Psychology
👫Unit 9 – Social Psychology
🗓️Previous Exam Prep
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.