Milo Chang
Minna Chow
Milo Chang
Minna Chow
AP Computer Science Principles ⌨️
80 resourcesSee Units
Basic List Operators
On the AP exam, you'll be asked to evaluate some basic operations on lists.
Remember, the AP Pseudocode's index starts at 1.
Accessing an element by index

This operation allows you to single out an element in a list based on its index number. You can then interact with only this element.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
print (grocery_list[0])The code's output:
milk
Assigning the value of an element of a list to a variable

This allows you to assign a variable to a certain element within a list, changing the element. Note that you wouldn't use this operation to add new values to the list, only to change ones already existing.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
change = "soap"
grocery_list[2] = change
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["milk", "eggs", "soap"]
Assigning a value to an element outright

Here's an example in Python:
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
grocery_list[2] = "fish"
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["milk", "eggs", "fish"]
Assigning the value of one element in the list to another

Like this!
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
grocery_list[0] = grocery_list[2]
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["cheese", "eggs", "cheese"]
Adding and Removing Elements
Inserting elements at a given index

This allows you to insert a value into the index position you want. It will increase the length of the list and shift everything greater than or equal to that index down by one place. For example, if you were to insert a new value at the index value 4, what was originally there will move to the index value 5, 5 will move to 6, and so on.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
grocery_list.insert (2, "butter")
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["milk", "eggs", "butter", "cheese"]
Adding elements to the end of the list

This allows you to add values to the end of your list.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
grocery_list.append ("flour")
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["milk", "eggs", "butter", "flour"]
Removing elements

You can also remove elements.
In Python, you remove items based on element value rather than index number.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
grocery_list.remove ("eggs")
print (grocery_list)The code's output: ["milk", "cheese"]
Determining the length of a list
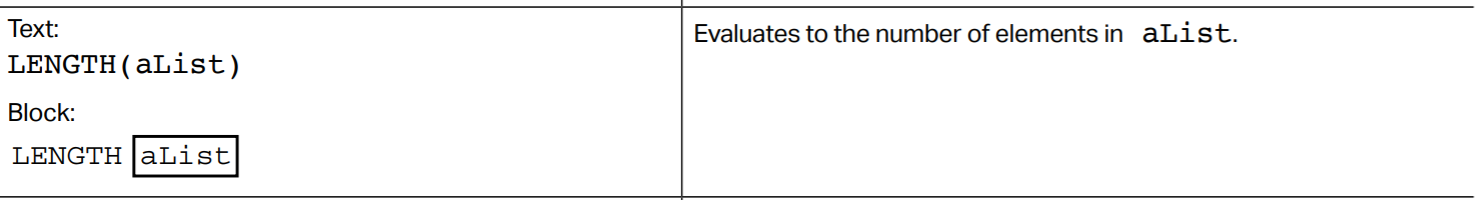
This will tell you what the length of your list is.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
print (len (grocery_list))The code's output: 3
Looping through Lists
You can also use loops to traverse, or go through, a list. This can either be a complete traversal or a partial traversal, depending on what your loop specifies.

Common algorithms used with lists will often find the maximum or minimum value inside the list or the average.
Linear search or sequential search algorithms check each element of a list, in order, until the desired value is found or all elements in the list have been checked.
Complete Traversal
In Python, you can perform a complete traversal of a list using either a for loop or a while loop. Both implementations are shown below.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
# for loop implementation
for element in grocery_list:
print(element)The code's output:
milk
eggs
cheese
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese"]
# while loop implementation
i = 0
while i < len(grocery_list):
print(grocery_list[i])
i += 1The code's output:
milk
eggs
cheese
Partial Traversal
In Python, you can also perform a partial traversal of a list using either a for loop or a while loop. Both implementations are shown below.
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese", "apples"]
# for loop implementation
start_index = 1
end_index = 3
for i in range(start_index, end_index + 1):
print(grocery_list[i])The code's output:
eggs
cheese
apples
grocery_list = ["milk", "eggs", "cheese", "apples"]
# while loop implementation
i = 1
while i < 4:
print(grocery_list[i])
i += 1The code's output:
eggs
cheese
apples
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🕹Unit 1 – Creative Development
⚙️Unit 2 – Data
📱Unit 3 – Algorithms & Programming
3.10Lists
- Basic List Operators
- Accessing an element by index
- Assigning the value of an element of a list to a variable
- Assigning a value to an element outright
- Assigning the value of one element in the list to another
- Adding and Removing Elements
- Inserting elements at a given index
- Adding elements to the end of the list
- Removing elements
- Determining the length of a list
- Looping through Lists
- Complete Traversal
- Partial Traversal
🖥Unit 4 – Computer Systems & Networks
⌨️Unit 5 – Impact of Computing
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
📝Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.