AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
Answers and Review for Multiple Choice Practice on Kinetics
⛔STOP ! ⛔ Before you look at the answers, make sure you gave this practice quiz a try so you can assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Unit 5. Click here for the practice questions: AP Chemistry Unit 5 Multiple Choice Questions

Image courtesy of Pixabay
Facts about the test: The AP Chemistry exam has 60 multiple choice questions and you will be given 1 hour 30 minutes to complete the section. That means it should take you around 15 minutes to complete 10 questions.
*The following questions were not written by College Board and although they cover information outlined in the AP Chemistry Course and Exam Description the formatting on the exam may be different.
1. When the rate of consumption of iron (II) is 15.0 M/s, what is the rate of production of the manganese (II) ion? Use the following balanced redox reaction:
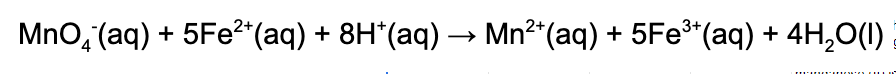
A. 3.0 M/s
B. 15.0 M/s
C. 5 M/s
D. 24.0 M/s
Explanation: Rates of change are stoichiometric. Therefore, since iron (II) and manganese (II) are in a 5 mol: 1 mol ratio, manganese (II) is produced at a rate of 3.0 M/s at that instant.
Read this guide to Redox Reactions!
2. A reaction is found to have the following mechanism, what is the order of the overall reaction with respect to substance A_2?
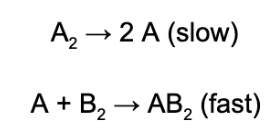
A. 0th
B. 1st
C. 2nd
D. 3rd
Explanation: The slow step for the mechanism is the first step. This means the rate law for this elementary step is equal to the overall reaction. The slow, elementary step has 1 for the coefficient for A_2; therefore, the reaction is first order with respect to A_2.
Read about writing rate laws here!
3. Which of the following correctly justifies why most chemical reactions slow down as they proceed?
A. As a reaction proceeds, there are less products.
B. As a reaction proceeds, there are less reactants.
C. As a reaction proceeds the temperature decreases.
D. As a reaction proceeds it consumes the catalyst.
Explanation: The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of the reactants. Because a chemical reaction consumes the reactants, the rate of the reaction decreases.
Read this guide about rate change!
4. A reaction is represented by the equation 2X + A -> XA + X. A plot of the concentration of A versus time, shown below, was found to have a negative slope. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
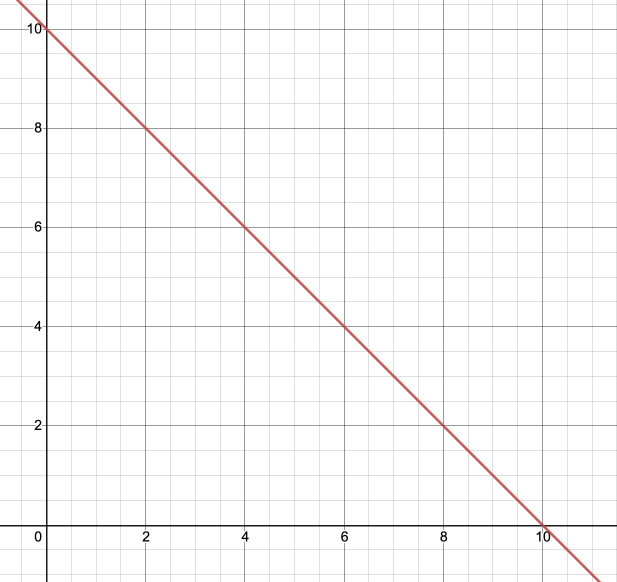
A. 0th
B. 1st
C. 2nd
D. 3rd
Explanation: Since the plot of [A] versus time is linear, this indicates the reaction is 0th order with respect to A.
Read this guide about rate change!
5. Based on the data, what is the concentration of the substance after 60 s?
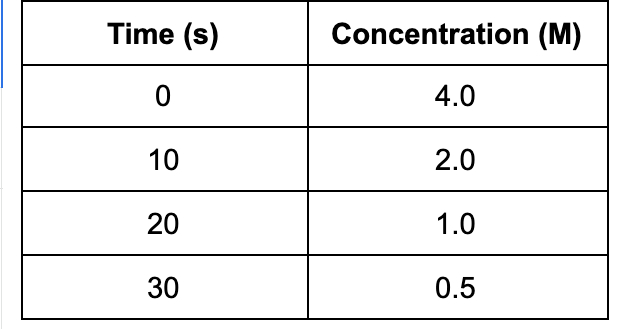
A. 0.125 M
B. 0.032 M
C. Need to know the order of the reaction.
D. 0.063 M
Explanation: The data shows the half life of the reaction is 10 s. Therefore, by dividing the concentration given by two a sufficient number of times, one finds the concentration at 60 s to be 0.063 M.
Watch this video about kinetics!
6. The following data table shows the concentration of a reaction and the initial rate data. Based on the table, what is the order of the reaction with respect to the reactant?
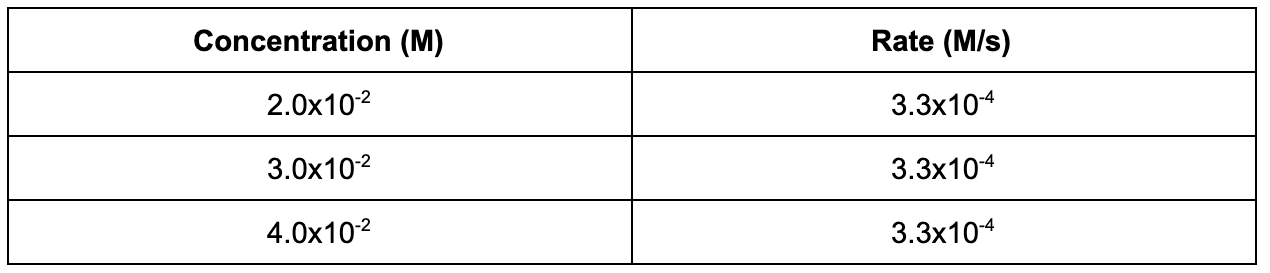
A. 0th
B. 1st
C. 2nd
D. 3rd
Explanation: Since the concentration of the reactant does not affect the rate of the reaction, the order of the reaction with respect to the reactant is 0th order.
Watch this video
7. Which of the following correctly justifies why a reaction is found to occur more quickly in a solution of 1.0M HCl?
A. The acid increases the temperature of the mixture causing the rate of collision between particles to increase.
B. The acid provides an alternative pathway for the reaction which increases the activation energy.
C. The acid acts as a catalyst, providing an alternative pathway for the reaction.
D. The acid solution increases the volume of the solution, decreasing the concentration of the reactants.
Explanation: A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction by providing an alternative pathway. This lowers the activation energy of the overall reaction.
Read this guide about catalysts!
8. A reaction is represented by the equation XA -> X + A. At a certain temperature, the rate constant is 2.5 1/M·s. What is the rate of the reaction if the initial [XA] = 1.1 M?
A. 2.8 M/s
B. 2.5 M/s
C. 3.0 M/s
D. Not enough information was provided.
Explanation: Based on the units for the rate constant, it's determined that the reaction is second order with respect to XA. The rate law is rate=k[XA]^2. Therefore, the rate of the reaction is rate= (2.5)(1.1)^2 = 3.0
Read this guide about rate change!
9. Which of the following defines the collision theory?
A. A reaction will only occur if the particles collide with the right amount of energy and in the right orientation.
B. Collisions between gas particles and other particles or the wall are elastic.
C. The energy created due to the collision between atoms in mass spectrometers.
D. The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Explanation: The collision theory states that a reaction will only occur if the reactants collide witht the right amounf of energy and in the right orientation.
Read this guide about the collision model!
10. Which of the following elementary reactions is first order with respect to A?
A. A+B->AB
B. AB -> A+B
C. A+A -> A_2
D. A_2 -> A+A
Explanation: An elementary reaction is one in which the coefficients of the reactants equal the order of the reaction with respect to the reactants. A + B -> AB is the only reaction where the coefficient for A is equal to 1.
Read this guide introducing rate laws!
11. The decomposition of diamond to graphite is thermodynamically favorable. Why does this reaction not occur at an observable rate?
A. Because diamonds cannot conduct electricity while graphite can.
B. The distance between the carbon atoms in diamonds are closer than the bonds between carbon in graphite.
C. A large amount of pressure is necessary for the reaction to occur.
D. The activation energy for the reaction is extremely high.
Explanation: The main reason a reaction does not occur at an observable rate, even when the reaction is thermodynamically favorable, is that the activation energy is very large.
Read this guide on reaction energy!
12. The following data table shows the concentration of a reaction and the initial rate data. Based on the table, what is the order of the reaction with respect to the reactant?
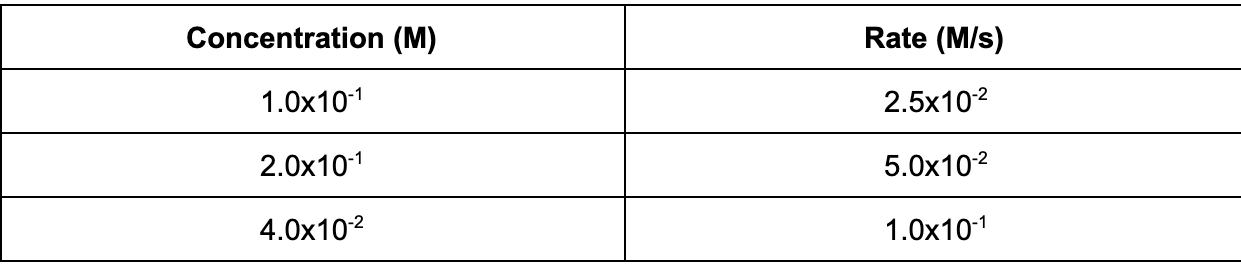
A. 2nd
B. 0th
C. 1st
D. 3rd
Explanation: The rate of the reaction changes the same as the change of the concentration of the reactant. When the reaction of the concentration doubles, the rate of the reaction doubles; therefore, the order of the reaction with respect to the reactant is 1st order.
Watch this video about kinetics!
13. Permanganate, a purple solution, reacts with hydrogen peroxide to produce a colorless solution. Which of the following methods is used to study the rate of reaction?
A. Photospectrometry
B. Mass Spectrometry
C. Gravimetric Analysis
D. Titration
Explanation: Since the solution changes from purple to clear, one can study the rate of disappearance of the color purple in solution using Beer's Law and photospectrometry.
Read this guide about Beer's Law!
14. What is the rate law for the overall reaction represented by the following mechanism?
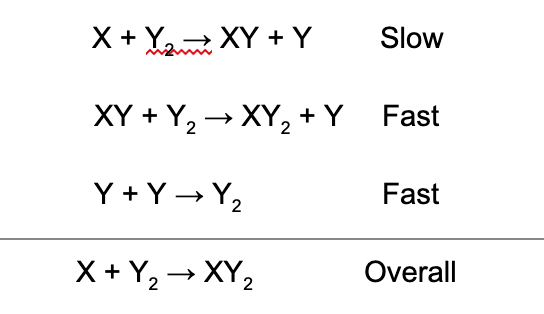
A. Rate = k[X][XY][Y]^2
B. Rate = k[X][Y_2]
C. Rate = k[XY][Y]
D. Rate = k[X]
Explanation: The slow, elementary step determines the rate of the overall reaction. Since the coefficients for X and Y_2 are 1 and 1 respectively, the exponents for X and Y_2 are 1 and 1.
Read this guide on elementary steps!
15. Given the data, what is the rate law for the reaction X + Z -> XZ?
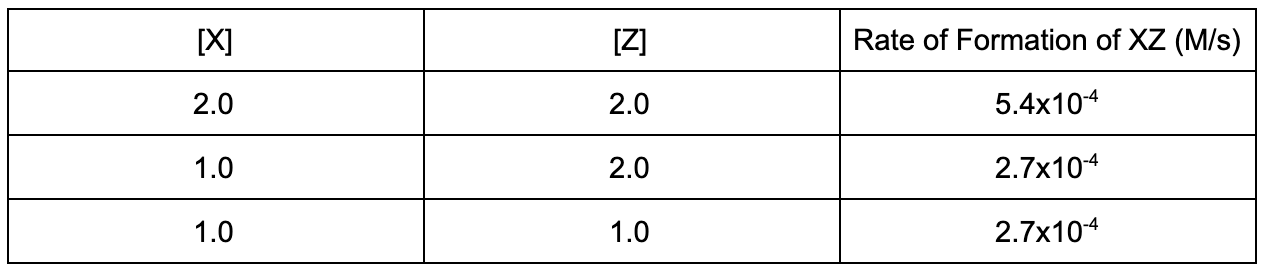
A. Rate = k[X]
B. Rate = k[Z]
C. Rate = k[X][Z]
D. Rate = k[X]^2
Explanation: When the concentration of X halved, the rate halved. When the concentration of Y halved, the rate did not change. Therefore, the reaction is 1st order with respect to X and 0th order with respect to Y.
Watch this video about kinetics!
What can we help you do now?
- 🔍Check out all of the resources for AP Chem Unit 6
- 🦘Jump to AP Chem Unit 6 Multiple Choice Questions
- 🤝Connect with other students studying AP Chem with Hours
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
✍️Free Response Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.