Catherine Liu
Catherine Liu
AP Chemistry 🧪
269 resourcesSee Units
Solid Matter Types & Properties
There are 4 major types of solid: molecular, covalent network, ionic, and metallic. Let's dive in!
In AP Chemistry, you learn about 3 main states of matter: solids, liquids, and gasses. While liquids and gasses are certainly important, in this article we're going to be discussing the properties and classification of solids and the 4 types of solids that you will have to be able to identify on the AP Chem exam.
1. Molecular Solids
Definition
- Molecular solids are made of molecules or atoms held together by intermolecular forces, not covalent bonds.
- Take ice, for example.
- Sure, each individual molecule is held together by covalent bonds, but the actual solid is created by hydrogen bonds connecting the molecules to each other.
Properties
- Intermolecular forces are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds, so molecular solids are relatively soft and flexible.
- This also means they tend to have low melting points.
- They do not conduct electricity because electrons are localized within individual molecules.
- Polar molecular solids, like sugar, will be soluble in water.
- Keep in mind that the individual molecules don't break apart, only the intermolecular forces do!
- Key properties to know: low melting point, do not conduct electricity
2. Covalent Network Solids
Definition
- Covalent network solids are held together by covalent bonds in a large network.
- They are different from molecular solids because atoms or molecules are covalently bonded to each other, not held together by intermolecular forces.
- Diamond and graphite are examples of covalent network solids made up of a network of carbon atoms:
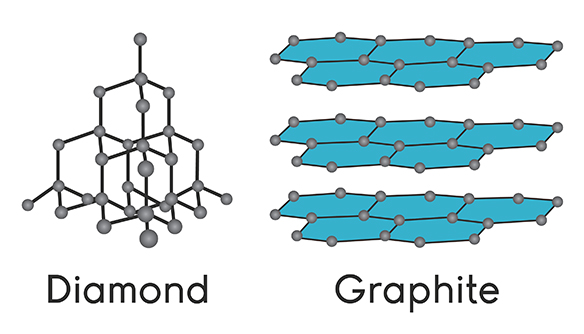
Source: Science Media Group
Properties
- They are usually hard and brittle.
- Covalent bonds are very strong, so covalent network solids typically have the highest melting points out of all four types of solids.
- They usually don't conduct electricity because valence electrons are localized within covalent bonds.
- An exception to this is graphite, where only three of four valence electrons are involved in the covalent network and the fourth is delocalized.
- They are insoluble in water.
- Key properties to know: hard, high melting points, do not conduct electricity (in all but few cases)
3. Ionic Solids
Definition
- Ionic solids are made up of oppositely charged ions held together by electrostatic attraction (a.k.a. ionic bonds).
- Electrostatic attraction just describes the attractive force between a positive charge and a negative charge.
- The strength of an ionic solid can be described by Coulomb's Law (Q = k(Q1Q2/r^2))
- Essentially, high charge + small ions = high electrostatic force
- The ions form a crystal lattice structure, seen in NaCl below:
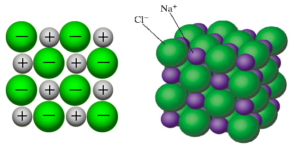
Properties
- They're hard and brittle.
- They have high melting points because ionic bonds require a lot of energy to break.
- In solid form, ionic compounds are poor conductors.
- When melted or dissolved in water, they will conduct electricity because they dissociate into individual ions that are free to move around.
- Not all ionic compounds are soluble, though, so keep those solubility rules in mind!
- Key properties to know: High melting points, conduct when dissolved BUT NOT AS SOLIDS!
4. Metallic Solids
Definition
- Metallic solids are metal atoms held together by metallic bonds.
- Metallic bonding is the sharing of a bunch of delocalized valence electrons that move freely throughout the solid. (sometimes called the "sea of electron" model)
- The metal atoms have a uniform distribution.
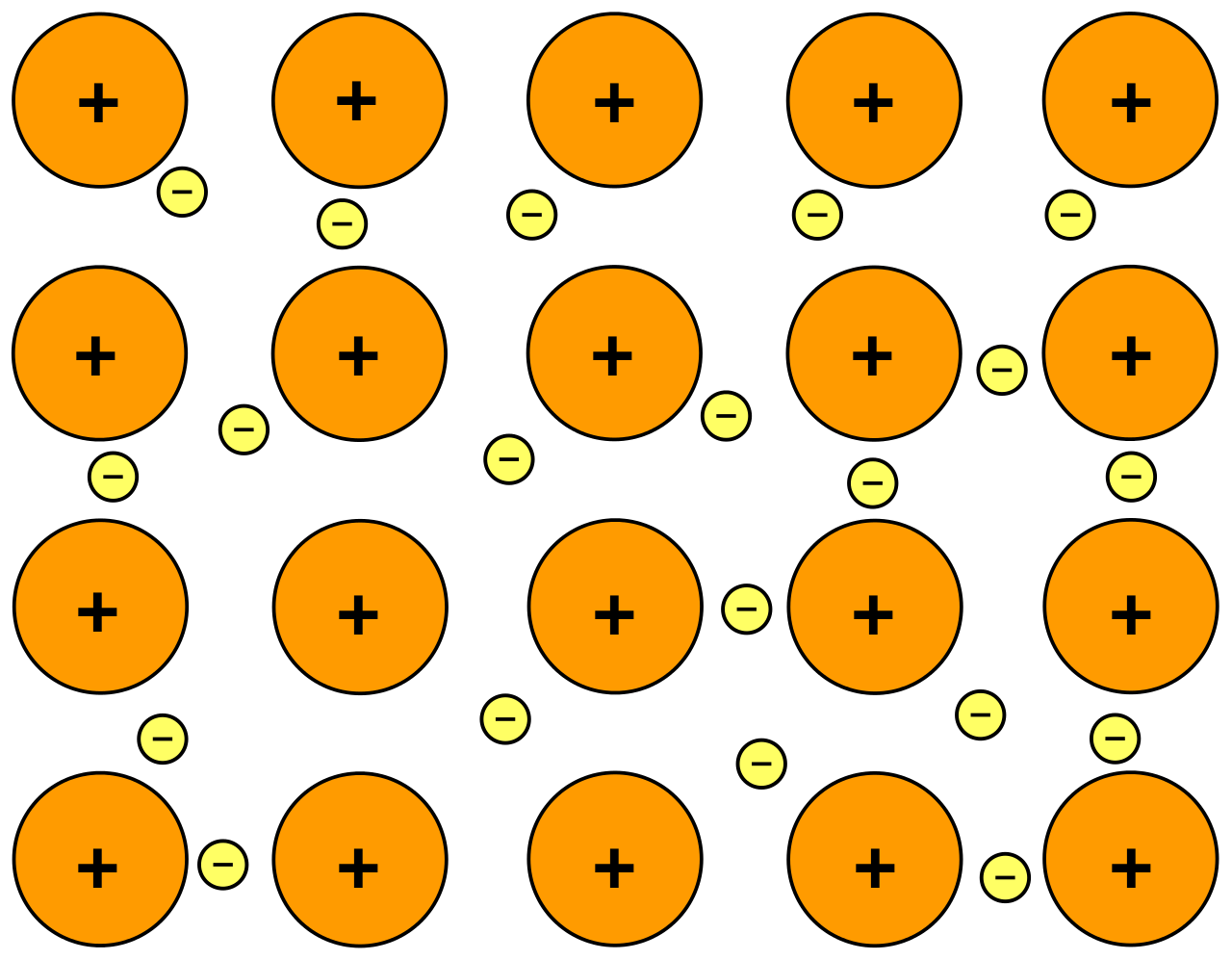
Properties
- Metallic solids vary a lot when it comes to melting points. Tungsten has the highest melting point at 3422°C, whereas mercury has the lowest at -38.83°C.
- They are shiny, strong, and malleable.
- They can conduct electricity because of their delocalized electrons.
- Adding another element to a metallic solid can form an alloy with new properties.
Congratulations! You now know about the properties of the 4 major types of solids in AP Chemistry. In applying this knowledge on the exam, you will be asked to identify a solid by its properties. For example, if I were to ask you what type of solid a compound was if it was brittle, melted at 1500 degrees, and conducted electricity when dissolved, you should know that this is an ionic solid. There are tons of practice questions out there just like this. Good luck!
Browse Study Guides By Unit
⚛️Unit 1 – Atomic Structure & Properties
🤓Unit 2 – Molecular & Ionic Bonding
🌀Unit 3 – Intermolecular Forces & Properties
🧪Unit 4 – Chemical Reactions
👟Unit 5 – Kinetics
🔥Unit 6 – Thermodynamics
⚖️Unit 7 – Equilibrium
🍊Unit 8 – Acids & Bases
🔋Unit 9 – Applications of Thermodynamics
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
✍️Free Response Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.