4.3 Adjusting An Argument to Address New Evidence
2 min read•january 30, 2023
Hayley Potter
Hayley Potter
AP English Language ✍🏽
224 resourcesSee Units
Unit 4 focuses on information! Analyze, analyze, and analyze some more!
Select evidence to make a claim you can use for your thesis.
Purpose and Audience--
The purpose of any written piece of work can and will be influenced by it's INTENDED AUDIENCE. The purpose of the text is specifically targeted and made for (say it again!) it's INTENDED AUDIENCE.
Considerations for a targeted audience can be general things such as age group, gender, and specific values. Values tend to be geared toward groups such as liberals, conservatives, Christians, or Muslims.
Prompt of the Text--
Prompts can help us figure out important information that we may not know already. Such as the date this text was written. When you know the date you can better analyze the values of the intended audience.
Language and TONE --
The diction (word choice) used can not only help us reveal the author's own educational level but the education level of their INTENDED AUDIENCE. Appeals matter too! Which appeals an author uses can also demonstrate the values of their intended audience.
Appeals are ethos, pathos, and logos!
Ethos- the author knows al ot about this topic, for sure more than the reader.
Pathos-the author wants their intended audience to have an emotional response to the text.
Logos- The author is making logical connections.
Occasion and Context--
Occasion comes from more than a simple urge to write, but rather from context (the magic word). Context of the period, which takes in account trends, issues, and culture. Figure out what the event was that made the writer feel the need to write.
Remember! Occasion is the whole event, no specifics all general. Exigence is that specific moment. Occasion is focused on the intended audience while exigence is concerning the writer.
Purpose--
This is possibly the biggest thing you want to focus on! What does the writer want the audience to understand!!!!!
This is serious business when it comes to the AP exam so do not slack on this! This is the writer's whole reason for writing!
Purpose comes from occasion and exigence because they set the stage for the purpose.
Let's use what we learned for a RA essay!
Use cause and effect by analyzing the occasion and exigence. This takes on the role of result and impact in your essay. Figure out the appeals the author has used! Use these too in your own RA essay! Your introduction should include as many aspects of SPACECAT that you can correctly analyze.
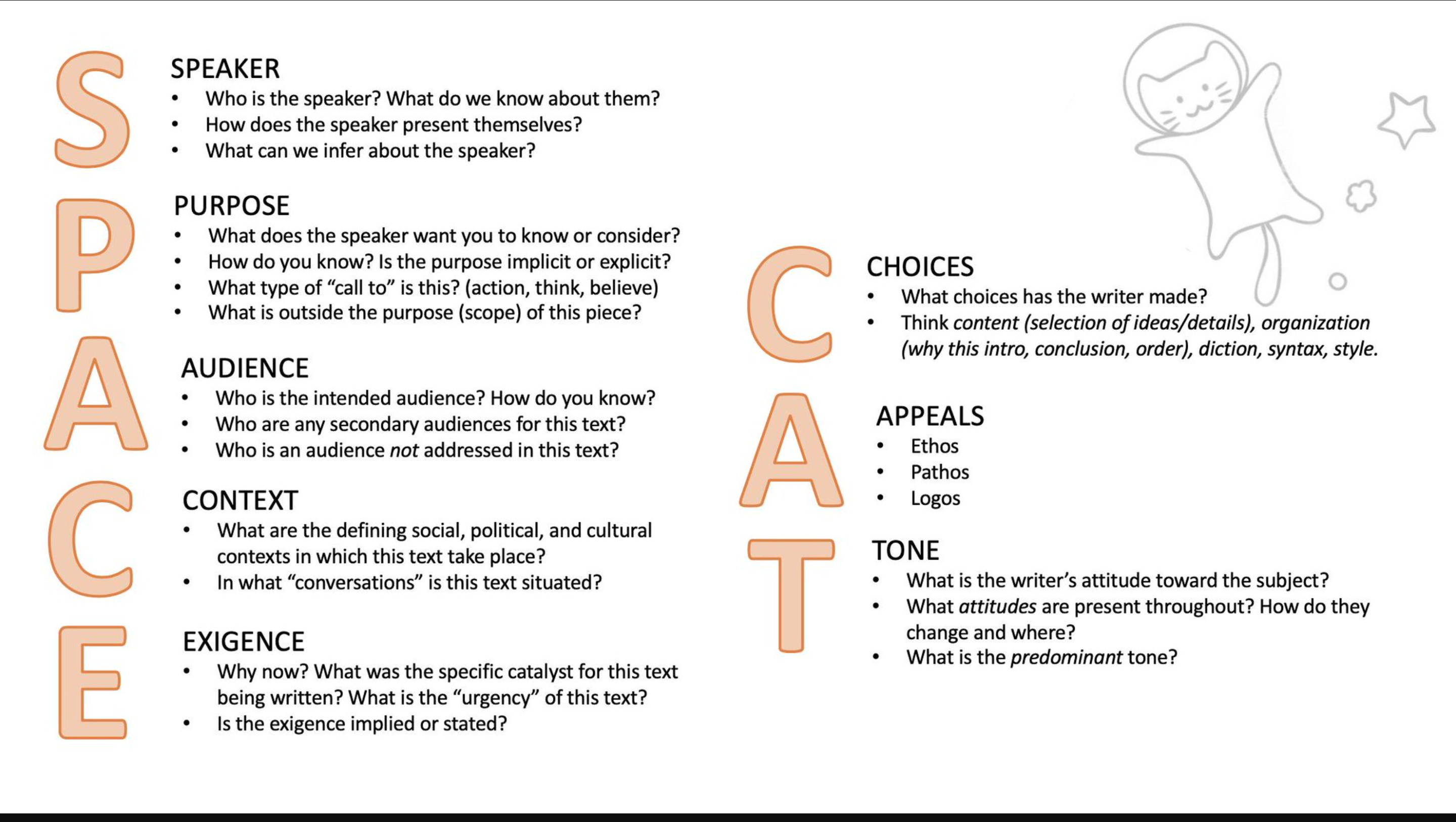
Tips--
*** Remember RA thesis is about the point the author wants to make to their intended audience.
Conclusion should include a connection to your own life to broaden your argument.
Always begin any argument with a claim, or a big opinion you want to prove to be true.
Reasoning explains why your claim is true.
Evidence provides proof your claim is true, use lots of evidence!!! Always pack on the evidence
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🧠Exam Skills
📑Exam Review - Synthesis Essay
📝Exam Review - Rhetorical Analysis Essay
💬Exam Review - Argument Essay
🧐 Multiple Choice Questions
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep
🥇Unit 1 – Claims, Reasoning, & Evidence
🗂️Unit 2 – Organizing Information for a Specific Audience
👀Unit 3 – Perspectives & How Arguments Relate
🔚Unit 4 – How writers develop arguments, intros, & conclusions
🎀Unit 5 – How a writer brings all parts of an argument together
👥Unit 6 – Position, Perspective, & Bias
🥊Unit 7 – Successful & Unsuccessful Arguments
😎Unit 8 – Stylistic Choices
😈Unit 9 – Developing a Complex Argument

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.